Group Policy Software Installation (GPSI) is one of the greatest gifts that Microsoft has given you! It is a free and semi-robust application deployment solution. Almost any organization can manage their entire application infrastructure with it. GPSI does have a few limitations though. One notable limit is the all or nothing redeployment option.
Wouldn’t it be awesome if you could selectively reinstall applications for a specific computer or for a small group of computers? Today, we are going to learn how to reinstall an application on a single machine and on multiple computers.
Reinstall a GPSI Application on a Single Machine
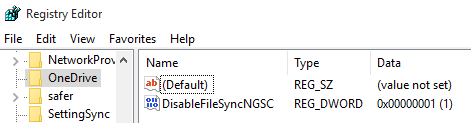
When you deploy an application through Group Policy, the local machine stores the GPSI information within HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionGroup PolicyAppMgmt . Each installed application has a unique ID assigned to it. This ID is the same for every machine. In the screenshot below, you can see an example of a deployed application named Mochasoft. It’s unique registry ID is {606…..}.
We can trigger an automatic reinstall by deleting the {606….} registry key and rebooting the machine. The Group Policy client will initiate a reinstall of the application at startup. Deleting a registry key this way can be a bit time consuming.
To make this easier, you can use a free app to list and delete these IDs. Before we continue, head over to the Tools page and download the MSI Manager App. It is located under the Active Directory/Group Policy section. Pin it to your Start Menu/Start Screen. You will use it often!
When you first launch MSI Manager, enter a computer name and press Scan. For testing, you can enter in your local machine name. MSI Manager will connect to the machine and list all of the GPSI applications. You can select an application and press Go to remove the registry entry and to trigger a GPUpdate.
The force reboot option will reboot the machine and allow the application to reinstall without waiting. If you have Verbose Mode enabled, you can even watch the application install. Go ahead and try this out on a machine. It is pretty sweet!
Reinstall a GPSI Application on Multiple Machines
Occasionally, you might need to reinstall an application on a small group of computers. Group Policy Registry Preferences can make this possible! In this example, we are wanting to reinstall our Mochasoft application on a specific lab of computers. In Active Directory, we will create a new security group namedReInstall_APP_Mochasoft and add our computers to this group.
Next, we will edit our APP_Mochasoft GPO which deploys our application. We will expand to Computer Configuration/Preferences/Windows Settings/Registry . Finally, we will create a new Registry Item and set the Action to Delete.
Under the keypath, we will enter SOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionGroup PolicyAppMgmtREGISTRY ID
To streamline this preference, we will click on the Common tab and check Apply once and do not reapply. We also want this preference to apply to our specific group of computers. We will select Item-level targeting and configure a new Security Group target that scopes this preference down to your ReInstall security group.
On the next GPUpdate, our machines will remove the specific GPSI registry key. On the next reboot, they will reinstall the application! This is how I selectively reinstall GPSI applications on specific computers and on computer groups.